CPU usage of Bitcoin Core peers
Wednesday, November 29, 2023To help improve partition resistance, a medium-term goal is to increase the number block relay connections a Bitcoin Core node has (see #28462). However, how much resources do block-relay connections use? Surely they are cheaper than full-relay connections? This blog-post focuses on the CPU usage of Bitcoin Core peers.
I’ve looked into this for CPU usage of peers - delvingbitcoin.org and PR #28463. This post is cross-posted from my answer on delvingbitcoin.org.
Methodology
To measure CPU usage of peers in Bitcoin Core, I’ve opted to measure the time we
spent in ProcessMessages() and SendMessages() per peer. I’ve added a
tracepoint to the end of both functions and pass, for example, the peer id, the
connection type, and function duration. I hook into these tracepoints with a
simple bpftrace script that prints each SendMessages() and
ProcessMessages() function call as CSV-formatted row. See this commit.
Setup
The underlying node is hosted on a VPS of a large cloud provider and has access to four AMD EPYC 7R32 cores (the message handling thread of Bitcoin Core is single-threaded and only uses one of these). The IP address of the node is well-known in the network. The node is pruned, which means no one was doing an IBD from the node. Other than pruning and debug logging enabled, the node is running with default parameters. The timing measurements posted here were all taken with all inbound slots filled (the per-peer measurements with about half-full inbound slots were similar). I’ve only looked at connections that that ended up being connected for more than a minute. This means, the data doesn’t cover short-lived feeler connections we made or received, and it doesn’t cover short-lived spy node connections that were evicted after a few seconds.
I’ve repeated these measurements on weekdays and a weekend in early November 2023. The resulting numbers differ slightly. This is likely related to, for example:
- transaction broadcast rate on the network ⇾ with more transactions being broadcast, we spent more time validating transactions, which is expensive (see below)
- number of
inbound full-relayvsinbound block-relay-onlyconnections ⇾inbound full-relayare more expensive thaninbound block-relay-onlyconnections (see below) - …
Total time spent sending and processing messages
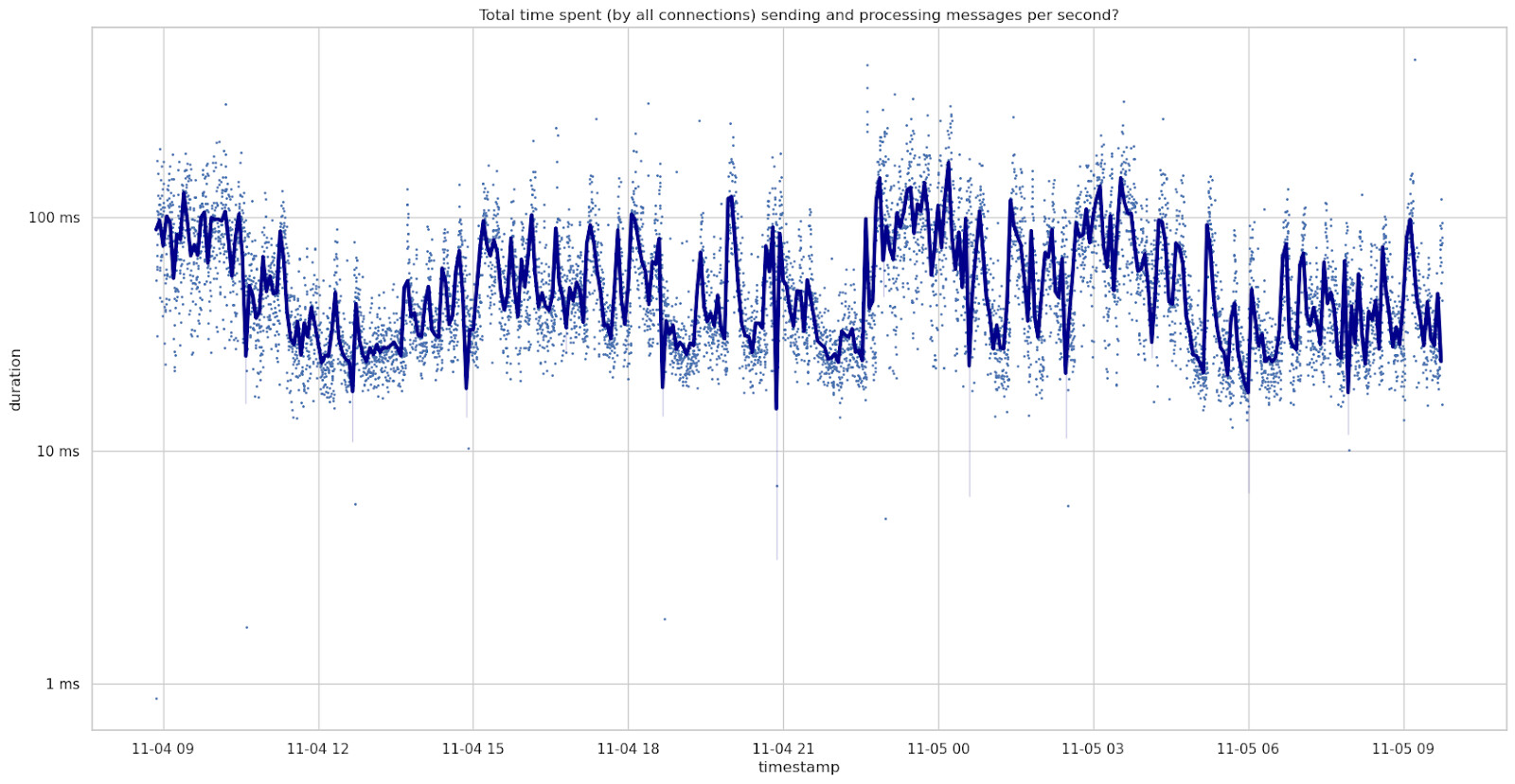
To start, this is the time spent per second in SendMessages() and
ProcessMessages() summed up for all peers.
On November 4th and 5th, the weekend before, it averaged at around 56ms per second.
On November 7th, a Tuesday, this averaged at about 32ms per second with 125 connections. This is on average about 17ms per second processing messages and 15ms per second sending messages.
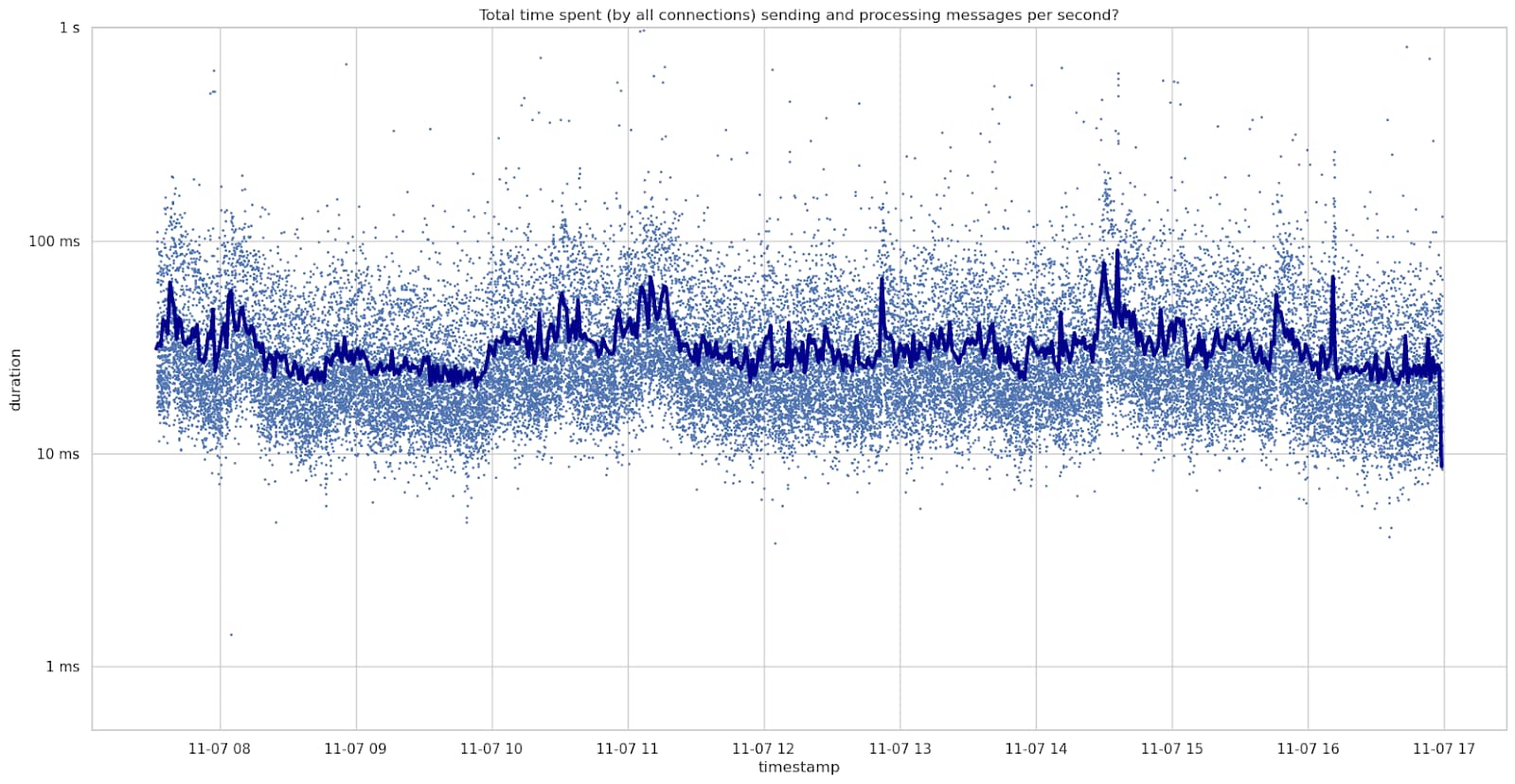
There were short periods with the total time per second reaching nearly 1000ms per second. This equals to 100% usage of one CPU core.
Per-peer time spent sending and processing messages
Looking at individual peers by connection direction and connection type shows
which connections are cheaper and which are more expensive. I assume that an
inbound connection sending me a version message with the f_realy flag set to
false is an outbound block-relay-only connection by the peer. While
-blocksonly nodes have the same fingerprint (link), I assume that these are rare and only marginally affect the
numbers.
November 4th and 5th: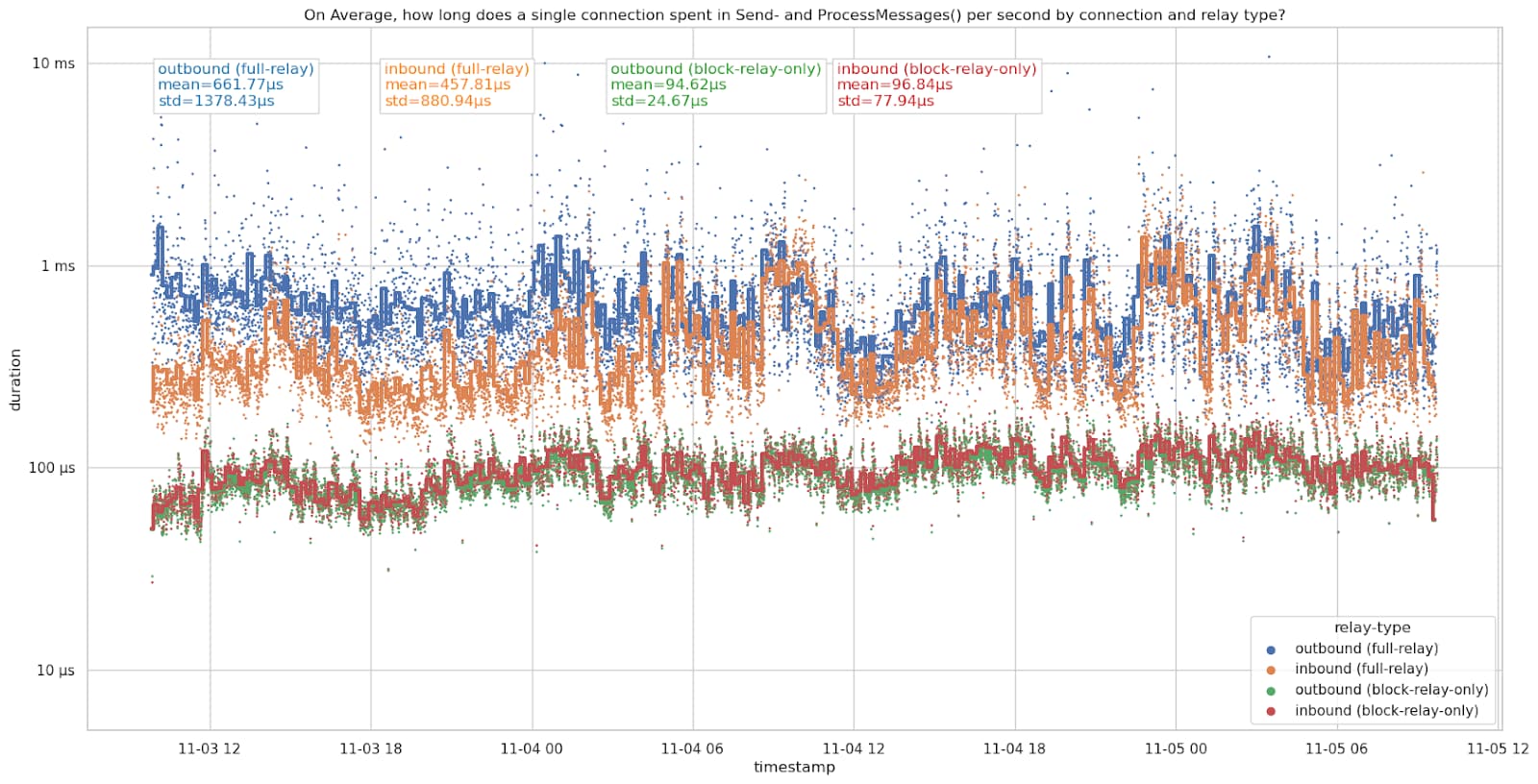
November 7th: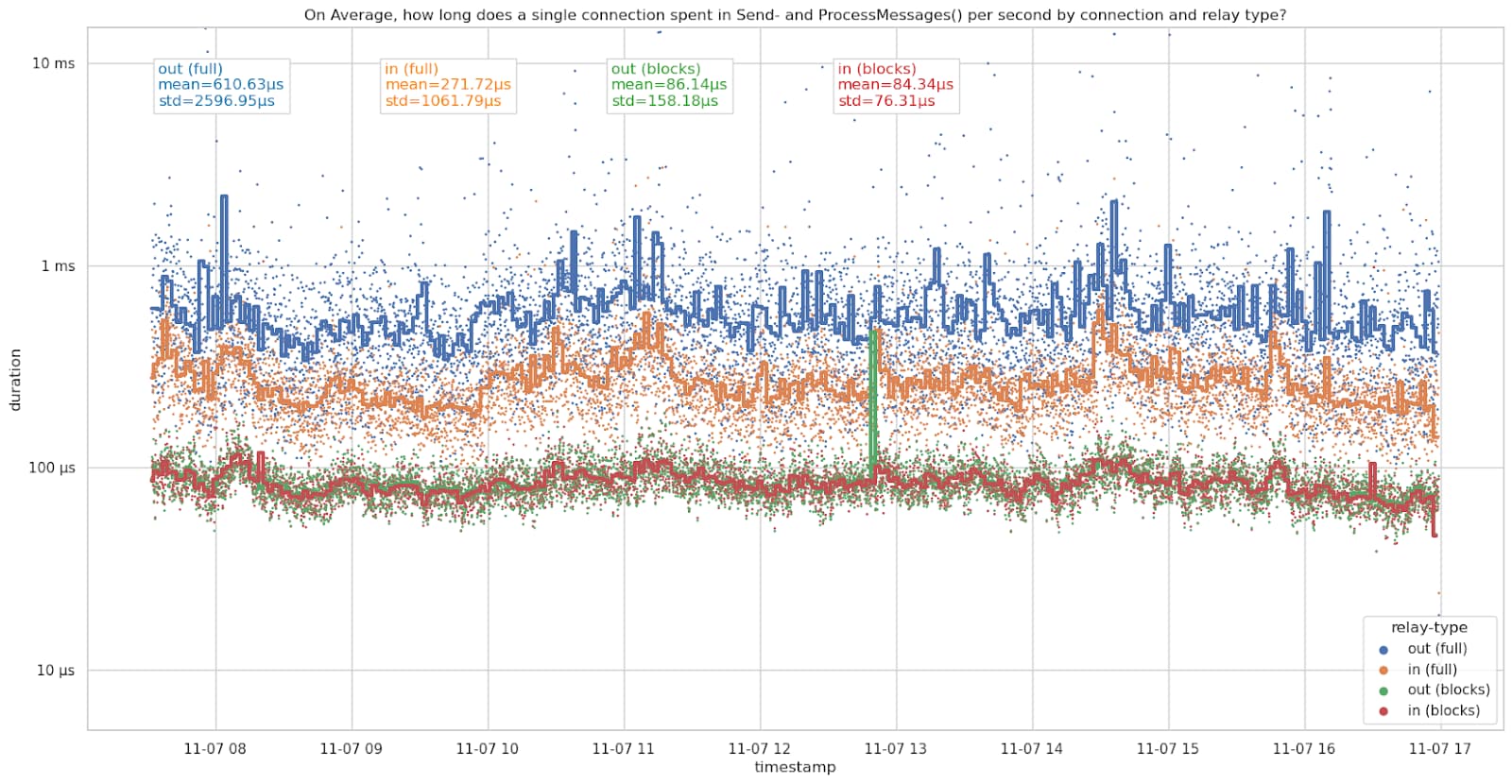
| connection type | mean 4th+5th ㅤㅤㅤ | mean 7th ㅤㅤㅤㅤ | stdev 4th+5th ㅤㅤㅤ | stdev 7th |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| outbound full-relay | 661.77µs | 611.63µs | 1378.43µs | 2596.95µs |
| inbound full-relay | 457.81µs | 271.72µs | 880.94µs | 1061.78µs |
| outbound block-relay-onlyㅤ | 94.62µs | 86.14µs | 24.67µs | 158.18µs |
| inbound block-relay-only | 96.84µs | 84.34µs | 77.94µs | 76.31µs |
ㅤ
The connections spend slightly less time on average on the 7th, but had a higher standard deviation. Likely related to differences in messages relayed on the network, however, I haven’t looked deeper into it.
Outbound full-relay connections are the most expensive connections here, taking more than 600µs per second on average. We currently only ever make 8 of these at a time. Inbound full-relay connections are cheaper than outbound full-relay connections, but still expensive compared to block-relay connections. However, we accept up to 114 inbound full-relay connections (typically about 91 due to some being block-relay-only, see also #28463 (comment)). Inbound and outbound block-relay-only connections spent just under 100µs sending and processing messages per second on average. These are the cheapest connections.
Time spent processing messages by relay type and connection direction
Since ProcessMessages() only ever processes one message at a time, we can
measure the processing time by received message. SendMessages() might send
zero, one, or multiple messages when called, which makes the same measurement
harder.
November 7th:
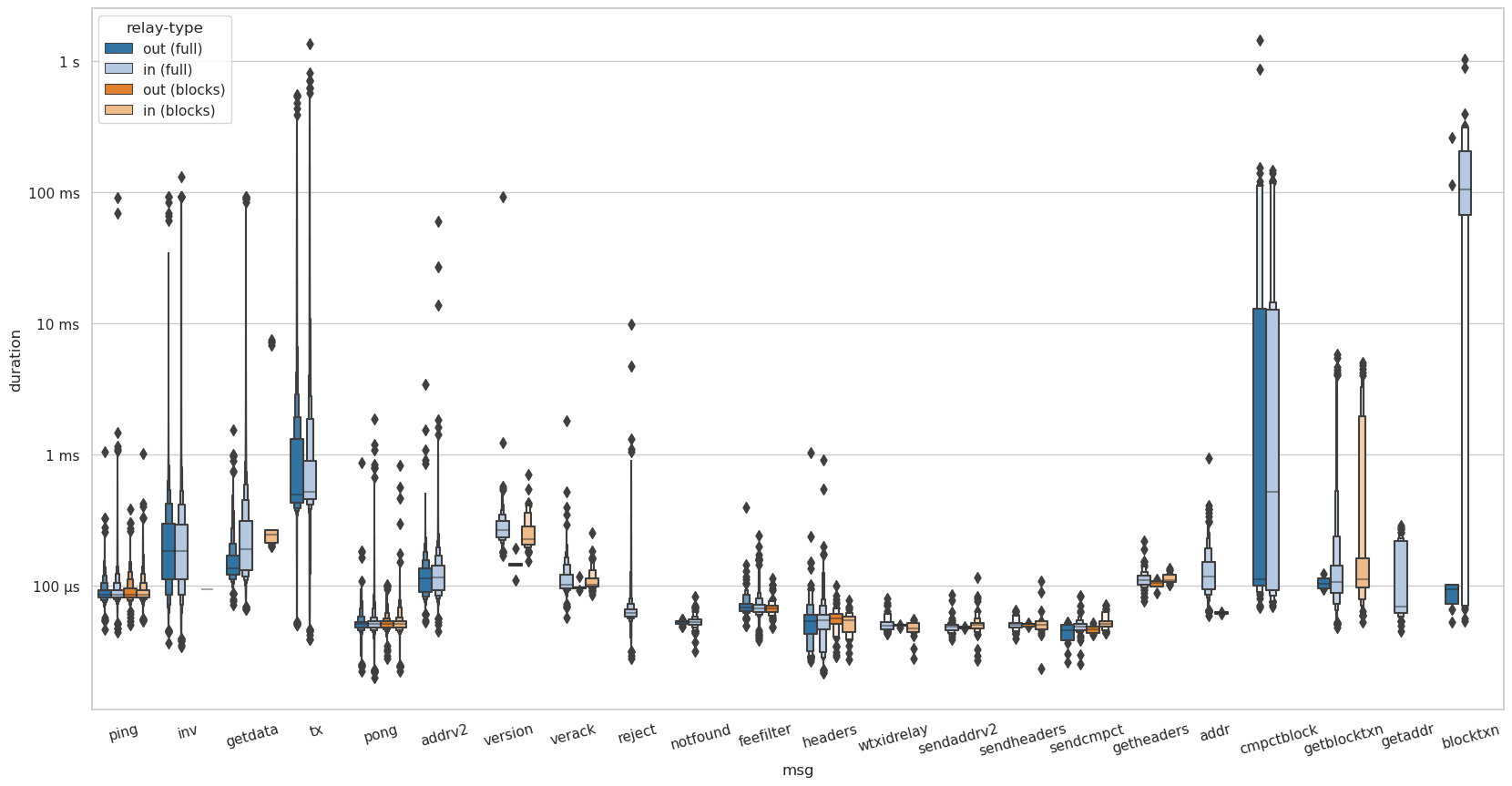
tx, addr, and addrv2 messages are only received and processed by
full-relay peers. Especially tx messages are expensive with close to 0.5ms in
median. While I received a few inv and getdata messages from
block-relay-only peers, the majority stems from full-relay peers. Additionally,
during this time-frame, all cmpctblock messages were received by full-relay
peers.
Inbound version messages take slightly shorter to process for block-relay-only
connections than for full-relay. @amiti suggested this might be related to
initializing the data structures for transaction relay?
Learnings
- On a modern server CPU core (AMD EPYC 7R32), Bitcoin Core usually spends less than 100ms (10%) of the time in the (single-thread) message handling thread with full inbound slots.
- Very roughly, an
outbound full-relayconnection (~600µs per second) has about 6x the CPU usage of anoutbound block-relay-onlyconnection (~100µs per second). Aninbound full-relayconnection (~300µs per second) has 3x the CPU usage of aninbound block-relay-onlyconnection (~100µs per second). - As to be expected: Time spent processing and sending messages per second is
lower for
block-relay-onlyconnections compared tofull-relay. Theblock-relay-onlyconnections don’t process and send transactions. On the processing side, transaction relay is more expensive than address relay.
Increasing number of block-relay-only slots and connections
#28463 proposes to increase the number of inbound connection slots for block-relay-only connections. Currently, a node has about 91 full-relay and 23 block-relay-only inbound connections (80% and 20% of 114). As currently proposed, the PR increases this to about 113 full-relay and 75 block-relay-only connections (60% and 40% of 189 = 200 - 2 - 1 - 8).
Assuming 600µs for a outbound full-relay connection, 300µs for an inbound full-relay and 100µs for a block-relay connection, currently we are at 34.6ms
per second and will be at 46.4ms (increase of 34%) with the proposed change.
6.6ms more due to the new full-relay connections and 5.2ms due to the
block-relay-only connections. While spending 46.4ms per second in the message
handling thread is probably fine, a more conservative change might be to leave
the number of full-relay inbound slots largely untouched. Here, RAM and
bandwidth usage should be considered too.
currently: $$ 8 \times 600µs + 2 \times 100µs + 91 \times 300µs + 23 \times 100µs = 34600µs = 34.6ms $$ as proposed: $$ 8 \times 600µs + 2 \times 100µs + 113 \times 300µs + 75 \times 100µs = 46400µs = 46.4ms $$
Since later increasing from 2 outbound block-relay connections to 8 as proposed in #28462 is only an increase of $ 6 \times 100µs $, I don’t see a problem with this from the CPU usage side.
Some notes
- It would also be useful to have these measurements for Erlay. Maybe Erlay makes transaction relay a lot cheaper (or a lot more expensive?).
- These measurements were made on a server CPU core, where a 34% increase is only about 11ms per second. However, the numbers might look very different on a nearly 70% slower Raspberry Pi 4 BCM2711 Core (see this comparison).
- Since my node is pruned, this does not include IBD data, which might raise the
average time spent in
SendMessages()(for both full-relay and block-relay connections). - Time spent in function isn’t a perfect measurement of CPU usage. For example, when sending requested blocks, a big chunk of the time might be spent waiting on disk IO.
Thanks to the MIT DCI for sponsoring the node I’ve used to measure this (and five more for related purposes!).

